
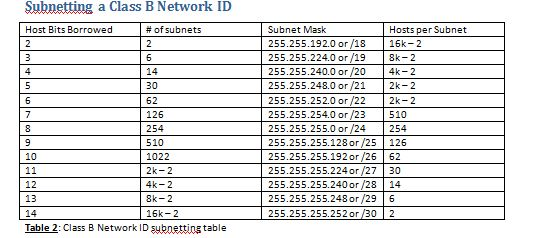
Subnetting allows us to create various sub-networks or logical networks within one network of a particular class of the network. Thus total usable IP’s are 32-3= 29 IP’s. Out of 32 IP’s, ideally one is used for the gateway, second is for the network IP and the third is for broadcast IP. If the IP is 10.68.37.128 (assuming class A case) #3) From the given subnet, we can also calculate the IP range of a particular network. Thus the network ID is 10 and the host ID is 20.12.2 The bits corresponding to all 0’s of the subnet mask is the host ID. #2) The bits corresponding to the subnet mask with all 1’s represent the network ID as it is a class A network and the first octet represents the network ID.
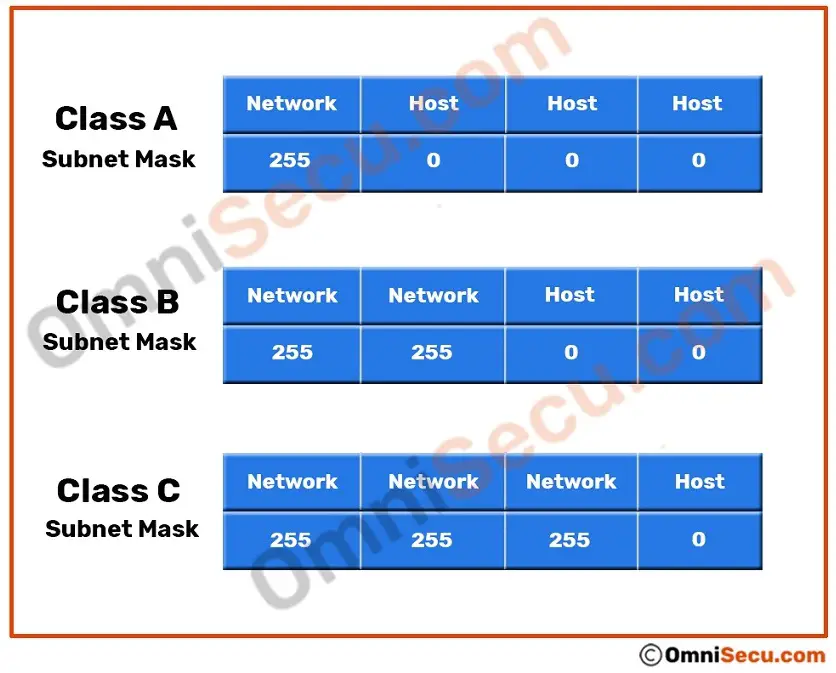
#1) Convert this Combination into a binary value: Let us assume the case of a class A IP address:įor Example, take a pair of IP address and subnet mask 10.20.12.2 255.0.0.0 Now let’s see how the mask will help us to classify the network ID and host ID part of an IP address. We have studied about the network class and subnet mask phenomenon of computer networking. The classification is shown with the help of the below table and figure. The first octet of an IP address identifies the particular class of an IP address.
By the categorization of a default subnet mask, we can easily identify the class of an IP address of the network. The organization which governs the internet has divided the IP addresses into different classes of the network.Įach class is identified by its subnet mask. Most popularly class A, B and C are used for commercial purposes and class D and E have reserved rights. As per the requirement, these are divided into various classes of a network called as class A, class B, class C, class D, and class E. Then see how we can calculate the IP address:ġ 0 0 1 0 0 0 1, 128+0+0+16+0+0+0+1= 145.īy combining the bits of the octets in different combinations according to the need, we can derive the overall IP address of the desired network. Suppose all the bits of an octet is not 1. The rightmost have the value 2^0 and left most have the value 2^7.Ģ^7 2^6 2^5 2^4 2^3 2^2 2^1 2^0 (^ denotes the power) There are 8 bits and each bit has the value of 2 to the power n (2^n). Let’s understand in detail how the binary octet values are converted into decimal values: The binary one is difficult to memorize thus, in general, the dotted decimal format is used worldwide for representation of the logical addressing. Thus it is represented in a dotted-decimal format.
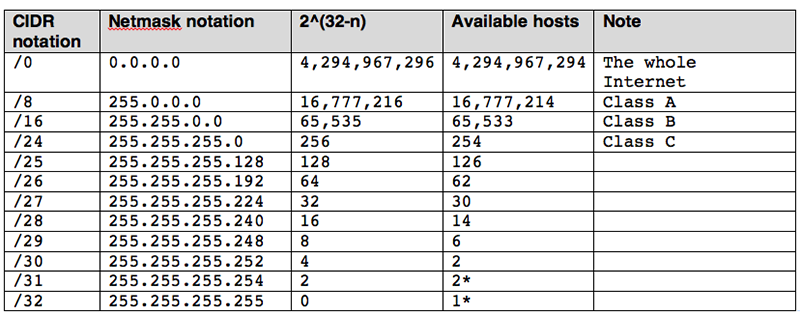
This octet is converted into decimal and is separated by a format i.e. It also has 4 octets as each octet is having 8 bits. The Network address and the Host address.

The 32 bits binary IP address is made up of two distinctive parts i.e. The host can be a computer, Mobile handset or even a tablet. The overall phenomenon of logical addressing works on the Layer-3 of the OSI reference model and the network components like routers and switches are the host devices that are most popularly used.Īn IP Address is a 32-bit logical address that distinctively classifies a host of the network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
